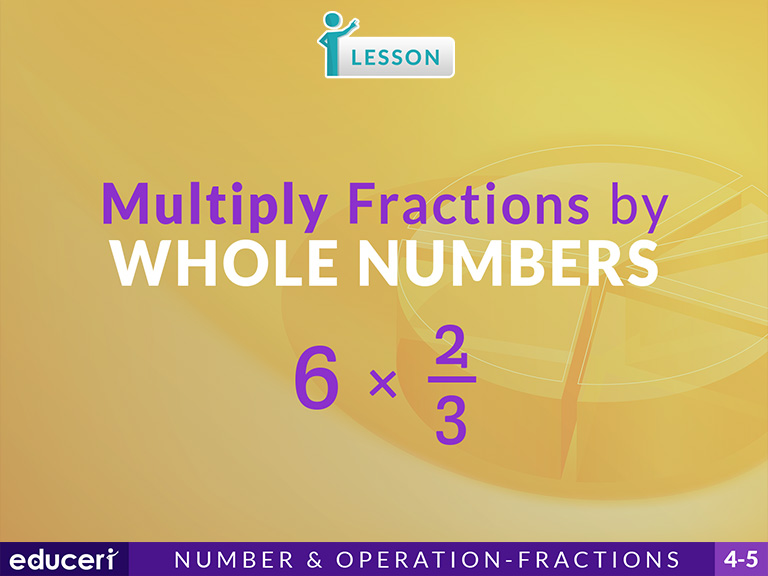
Standard Alignments:
4.NF.4.B Understand a multiple of a/b as a multiple of 1/b, and use this understanding to multiply a fraction by a whole number. For example, use a visual fraction model to express 3 × (2/5) as 6 × (1/5), recognizing this product as 6/5. (In general, n × (a/b) = (n × a)/b.)
5.NF.4.A5.NF.4.A Interpret the product (a/b) × q as a parts of a partition of q into b equal parts; equivalently, as the result of a sequence of operations a × q ÷ b. For example, use a visual fraction model to show (2/3) × 4 = 8/3, and create a story context for this equation. Do the same with (2/3) × (4/5) = 8/15. (In general, (a/b) × (c/d) = (ac)/(bd).