All Lessons

Use Fact Families
(D) Apply basic fact strategies to add and subtract within 20, including making 10 and decomposing a number leading to a 10
1.5.G(G) Apply properties of operations to add and subtract two or three numbers.
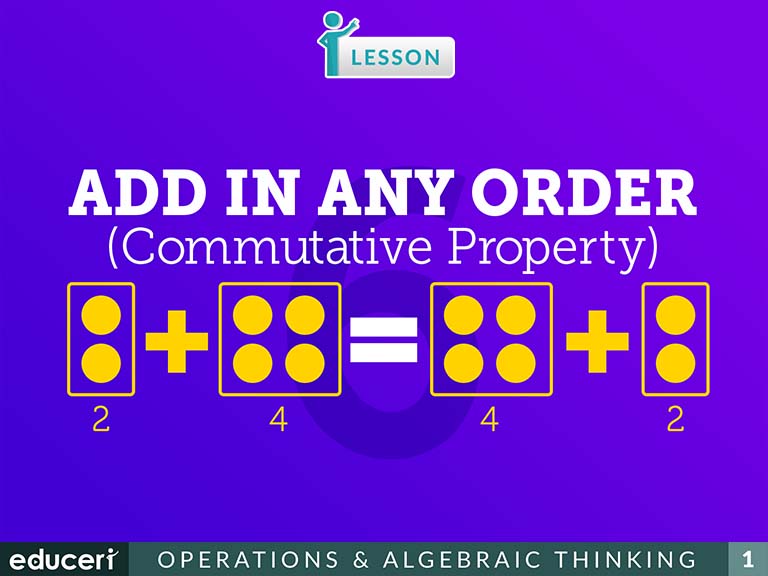
1.OA.3 Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract. Examples: If 8 + 3 = 11 is known, then 3 + 8 = 11 is also known. (Commutative property of addition.) To add 2 + 6 + 4, the second two numbers can be added to make a ten, so 2 + 6 + 4 = 2 + 10 = 12. (Associative property of addition.)
1.OA.41.OA.4 Understand subtraction as an unknown-addend problem. For example, subtract 10 - 8 by finding the number that makes 10 when added to 8.
2.OA.22.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers.
Share This Lesson
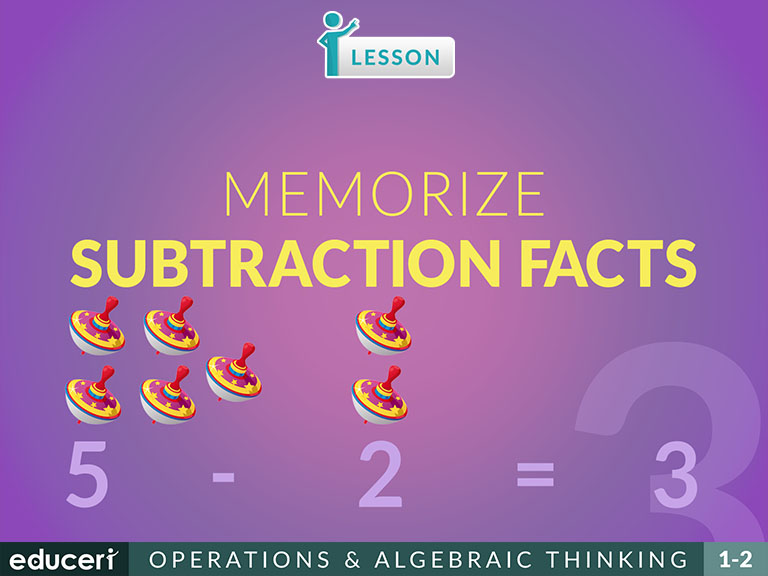
Memorize Subtraction Facts
This operations and algebraic thinking lesson covers how to memorize subtraction facts. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students will practice the subtraction facts of numbers 2 through 10 by a combination of reading aloud and writing each fact many times in horizontal and vertical formats.
Share This Lesson

Solve Addition Equations
This algebra and functions lesson focuses on writing addition number sentences. The lesson includes research-based strategies and questions that help prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students read the word problem and identify addition key words and number words. Then, they write an addition number sentence and practice reading aloud. In addition to the lesson, there are four pages of Independent Practice and review with questions modeled after current adaptive testing items.
Share This Lesson

Write Subtraction Equations
Share This Lesson

Use the Equal Sign
This algebra and functions lesson focuses on using the equal sign. The lesson includes research-based strategies and questions that help prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students read the problem and complete the math fact. Then, they determine whether the two numbers are equal or not equal using the appropriate symbols. Finally, students interpret the answer using the math fact. In addition to the lesson, there are four pages of equal sign flash cards and eight pages of Independent Practice and review with questions modeled after current adaptive testing items.
Share This Lesson

Create Story Problems (Addition & Subtraction)
Share This Lesson
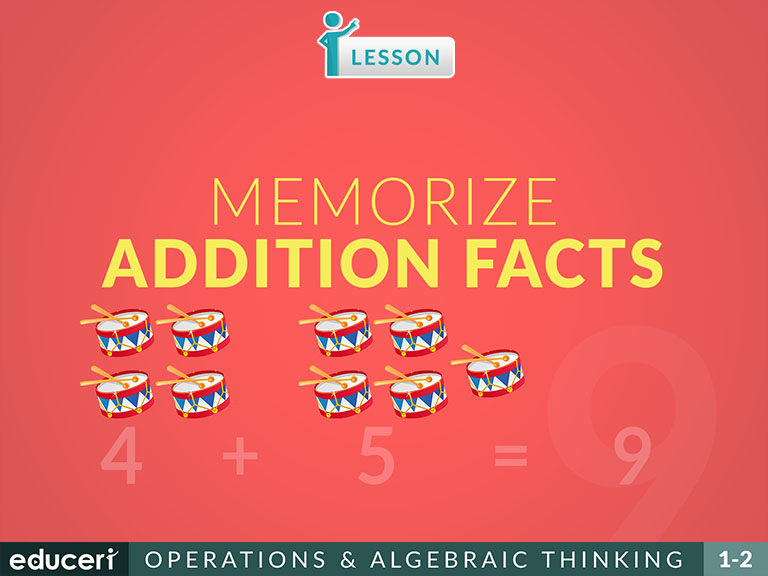
Memorize Addition Facts
This operations and algebraic thinking lesson covers how to memorize addition facts. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students will practice the addition facts of numbers 2 through 10 by a combination of reading aloud and writing each fact many times in horizontal and vertical formats.
Share This Lesson

Subtract Numbers by Counting Down
This operations and algebraic thinking lesson covers subtracting numbers by counting down. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students read the subtraction problem and then subtract the numbers by counting down. A number chart is provided to keep them on track. Word problems are also used. They finish by reading the fact family aloud.
Share This Lesson

Determine if Equations are True or False
(E) Understand that the equal sign represents a relationship where expressions on each side of the equal sign represent the same value(s)
2.4.A(A) Recall basic facts to add and subtract within 20 with automaticity
(Y1) Represent and solve simple addition and subtraction problems using a range of strategies including counting on, partitioning and rearranging parts (ACMNA015)
ACMNA030(Y2) Solve simple addition and subtraction problems using a range of efficient mental and written strategies (ACMNA030)
1.OA.7 Understand the meaning of the equal sign, and determine if equations involving addition and subtraction are true or false. For example, which of the following equations are true and which are false? 6 = 6, 7 = 8 - 1, 5 + 2 = 2 + 5, 4 + 1 = 5 + 2.
2.OA.22.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers.
From CCSS "For example, which of the following equations are true and which are false? 6 = 6, 7 = 8 – 1, 5 + 2 = 2 + 5, 4 + 1 = 5 + 2."
Share This Lesson

Add Three Numbers
Retrofit the existing lesson of adding three numbers to include word problem applications.
Share This Lesson

Count and Write Numbers to 120
This number and operations in base ten lesson covers how to count and write numbers to 120. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students will read the numbers in a number chart and write in missing numbers.
Share This Lesson

Count and Write Numbers to 50
This number and operations in base ten lesson covers how to count and write numbers to 50. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students will read the numbers in a number chart and write in missing numbers.
Share This Lesson

Count Objects 100-120
This number and operations in base ten lesson covers how to count objects from 100 to 120. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students will read sentences that describe a specific number of objects in a group. Then, they will count on from that total to add a certain number more.
Share This Lesson

Count Objects 20-100
This number and operations in base ten lesson covers how to count objects from 20 to 100. The lesson includes research-based strategies and strategic questions that prepare students for assessments. In this lesson, students will read sentences that describe a specific number of objects in a group. Then, they will count on from that total to add a certain number more.